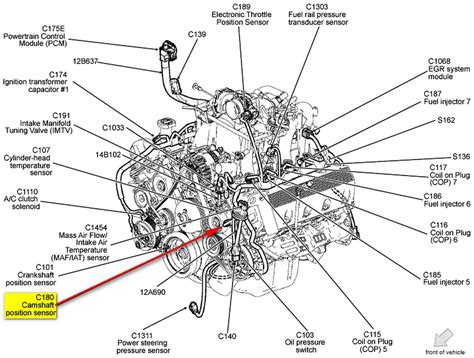
Learn about the camshaft position sensor, its importance, symptoms of failure, diagnostic processes, and how to replace it effectively for optimal vehicle performance.If you own a 2010 Ford F-150, understanding the camshaft position sensor (CPS) is essential for maintaining your truck’s performance. The CPS plays a crucial role in regulating the engine’s timing and overall efficiency, and its location, especially on bank 2, can be a source of confusion for many owners and mechanics alike. In this blog post, we will delve into the significance of the camshaft position sensor, particularly focusing on the important bank 2 location. We will also cover the symptoms that may indicate sensor failure, the diagnostic steps to pinpoint issues, and guidance on replacing the CPS. By the end of this post, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge needed to tackle any camshaft position sensor concerns you may encounter with your F-150.
Understanding the Camshaft Position Sensor
The camshaft position sensor plays a crucial role in the operation of an engine. This sensor monitors the position and speed of the camshaft, providing essential data to the engine control unit (ECU) for optimal engine performance. Understanding how this component works can help you diagnose engine issues more effectively.
Typically located near the camshaft, the sensor uses either a Hall effect or magnetic technology to determine the camshaft’s rotational position. By sending this information to the ECU, the camshaft position sensor helps regulate engine timing, fuel delivery, and ignition timing.
Importance of the Camshaft Position Sensor
The camshaft position sensor is vital for the following reasons:
- Engine Timing: Ensures that the valves open and close at the right times, allowing for efficient combustion.
- Fuel Efficiency: Helps the ECU adjust fuel injection for better mileage.
- Emissions Control: Aids in minimizing harmful emissions by optimizing combustion processes.
- Performance: Maintains smooth engine operation and enhances overall performance.
When the camshaft position sensor fails, it can lead to a range of issues, from rough idling to complete engine failure. Therefore, knowing the signs of a malfunctioning sensor is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s health.
A well-functioning camshaft position sensor is key to a smooth running engine. – Automotive Expert
For those working on a 2010 Ford F150, familiarity with the camshaft position sensor’s location—especially for Bank 2—is essential for effective diagnostics and repairs.
Importance of Bank 2 Location
The camshaft position sensor plays a crucial role in controlling the timing of your vehicle’s engine, particularly in multi-cylinder engines like the 2010 Ford F150. Understanding the significance of the Bank 2 location for the camshaft position sensor is essential for optimal engine performance.
Bank 2 refers to the side of the engine that does not contain the first cylinder. For the V8 engine in the 2010 Ford F150, this means that Bank 2 will have cylinders 2, 4, 6, and 8, while Bank 1 has cylinders 1, 3, 5, and 7. The location of the camshaft position sensor is vital to ensure accurate readings and synchronization with the crankshaft.
Why Bank 2 Location Matters
- Engine Timing: The camshaft position sensor in Bank 2 helps maintain accurate engine timing, which is essential for efficient combustion.
- Fuel Efficiency: A properly functioning sensor ensures that the engine runs smoothly, maximizing fuel efficiency.
- Emissions Control: Accurate readings from the sensor help in reducing harmful emissions by optimizing fuel mixture.
- Diagnostic Capability: Knowing the Bank 2 location allows mechanics to quickly diagnose potential issues with the camshaft and engine timing.
Critical symptoms of a failing camshaft position sensor, especially located in Bank 2, may include:
1. Check engine light illumination.
2. Rough idling or stalling.
3. Decreased acceleration.
4. Increased emissions.
In conclusion, being aware of the Bank 2 location of the camshaft position sensor in the 2010 Ford F150 is vital for maintaining engine performance and diagnosing potential issues. Regular checks and maintenance can help prevent costly repairs and ensure that the engine operates at its best.
Symptoms of Camshaft Position Sensor Failure
The camshaft position sensor is an essential component in your vehicle’s engine management system, particularly in 2010 Ford F150s. When this sensor begins to fail, it can lead to a variety of symptoms that affect your vehicle’s performance. Recognizing these symptoms early can help you avoid more significant issues down the road.
- Engine Misfires: A failing camshaft position sensor may cause the engine to misfire, as it struggles to correctly time the ignition and fuel injection events.
- Rough Idle: You might notice your engine idling roughly or inconsistently when the sensor is malfunctioning.
- Check Engine Light: One of the most common indications of sensor failure is the illumination of the Check Engine Light on your dashboard. A diagnostic scan can help determine if it’s related to the camshaft position sensor.
- Decreased Fuel Efficiency: If the sensor is providing inaccurate information, the engine may run inefficiently, leading to decreased fuel economy.
- Difficulty Starting the Engine: A compromised camshaft position sensor can lead to challenges with starting the engine, as it may not send the correct signals to the engine control module (ECM).
- Stalling: In some cases, your F150 may stall unexpectedly, particularly if the engine is under load or during acceleration.
If you experience any of the above symptoms, it’s highly recommended that you have your vehicle checked by a qualified mechanic. Prompt diagnosis and repair can save you time and money by preventing extensive engine damage and ensuring your 2010 Ford F150 operates smoothly.
Diagnostic Process for Bank 2 Location
Diagnosing the Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP) located at Bank 2 of a 2010 Ford F150 is a vital process, as it can greatly affect the engine’s performance. Below, we outline a structured diagnostic approach to pinpoint issues related to the Bank 2 camshaft position sensor.
Step 1: Preliminary Inspection
Start with a visual inspection of the engine bay, focusing on:
- Wiring and connectors of the Camshaft Position Sensor for any signs of damage.
- Physical state of the Bank 2 camshaft position sensor.
- Any fluid leaks that may affect sensor wiring.
Step 2: Use of Diagnostic Tools
To diagnose the Bank 2 camshaft position sensor:
- Connect an OBD-II scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Check for trouble codes related to the camshaft position sensor.
- Take note of any DTCs (Diagnostic Trouble Codes) that indicate sensor issues alluding to Bank 2.
Step 3: Checking Sensor Voltage
To ensure the sensor is receiving proper voltage:
Using a multimeter, measure the voltage at the Camshaft Position Sensor connector. You should expect readings between 4.5V to 5.5V.
Step 4: Examining Sensor Output Signal
Check the signal output from the sensor:
- Start the engine and monitor the signal with an oscilloscope.
- A healthy signal will typically appear as a square wave.
- Compare the waveform to a reference chart for the 2010 Ford F150.
Step 5: Camshaft Timing Check
Verify if the camshaft timing is correctly aligned:
- Use timing tools or marks to ensure that the camshaft and crankshaft timing align correctly.
- If misaligned, this could indicate a mechanical issue affecting the Bank 2 camshaft position sensor.
Step 6: Clear Codes and Road Test
After completing the tests:
- Clear any DTCs from the system.
- Conduct a road test to see if the codes reappear.
Using this diagnostic process will help ensure that any issues with the Bank 2 camshaft position sensor are correctly identified and resolved, maintaining the efficiency and performance of your 2010 Ford F150.
Replacing the Camshaft Position Sensor
Replacing the Camshaft Position Sensor on your 2010 Ford F150 can be a straightforward process if you follow the correct steps. The camshaft position sensor is crucial for ensuring your vehicle’s engine provides optimal performance by relaying the position of the camshaft to the engine control unit (ECU).
Tools and Materials Needed
- Socket set
- Torque wrench
- Ratchet
- Screwdriver
- New camshaft position sensor
- Engine oil
Steps to Replace the Camshaft Position Sensor
- Safety First: Ensure the engine is turned off and cool before beginning any work.
- Disconnect the Battery: Remove the negative terminal of the battery to prevent any electrical shorts.
- Locate the Sensor: The Bank 2 camshaft position sensor is usually located on the passenger side of the engine near the top of the valve cover.
- Remove the Connector: Gently disconnect the wiring harness from the sensor by pressing the release tab and pulling it off.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Use a socket or ratchet to remove the bolts securing the sensor in place. Carefully take the sensor out.
- Prepare the New Sensor: Apply a small amount of engine oil to the O-ring of the new camshaft position sensor for a better seal.
- Install the New Sensor: Position the new sensor in place and tighten the bolts to the manufacturer’s specified torque. Ensure it is snug but do not overtighten.
- Reconnect the Wiring Harness: Firmly attach the wiring harness back to the new sensor until you hear a click.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reattach the negative battery terminal and ensure it is secure.
- Check Your Work: Start the engine and ensure that there are no warning lights on the dashboard. If the engine runs smoothly, the replacement was successful.
Tips for a Smooth Replacement
It’s always a good idea to consult your vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions regarding the 2010 Ford F150. This will give you a clearer understanding of the location and any additional steps needed for your specific model.
By following these steps, you can successfully replace the camshaft position sensor and help maintain the performance of your Ford F150.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a camshaft position sensor and why is it important?
The camshaft position sensor monitors the position of the camshaft in relation to the crankshaft, allowing the engine control unit to optimize timing for better performance and efficiency.
Where can I find the bank 2 camshaft position sensor on a 2010 Ford F150?
The bank 2 camshaft position sensor on a 2010 Ford F150 is typically located on the back side of the engine near the intake manifold, close to the firewall.
What are the symptoms of a failing camshaft position sensor?
Symptoms can include poor acceleration, engine misfires, reduced fuel efficiency, engine stalling, and the check engine light illuminated.
How do you diagnose a faulty camshaft position sensor?
To diagnose a faulty camshaft position sensor, you can use an OBD-II scanner to check for related error codes, conduct a visual inspection of the sensor and its wiring, and perform a resistance test to ensure it is functioning properly.
What tools do I need to replace the camshaft position sensor?
Common tools include a socket set, a wrench set, a screwdriver, and possibly a torque wrench, along with safety equipment like gloves and goggles.
Can I drive my 2010 Ford F150 with a bad camshaft position sensor?
While you can drive with a bad camshaft position sensor, it is not advisable as it may cause poor engine performance, increased emissions, and potentially lead to further engine damage.
Is it difficult to replace the camshaft position sensor on a 2010 Ford F150?
The difficulty can vary; while some may find it straightforward, accessing the sensor may require removing other components, so it can be moderately challenging for someone without automotive experience.